What Is BMS on a Lithium Battery? A Complete Guide to Its Role, Benefits, and Usage
- Introduction: What Is BMS on a Lithium Battery?
A BMS, short for Battery Management System, is an electronic control unit that monitors and manages the operation of a lithium battery. It ensures the battery works within safe limits, prevents damage from extreme conditions, and maximizes the lifespan of the cells.
Think of it as the “brain” of the battery pack—constantly checking voltage, current, and temperature while making decisions to protect the battery. Whether you are powering an electric vehicle, running a solar energy system, or starting a motorcycle with a LiFePO₄ battery, the BMS silently works behind the scenes to keep everything safe and reliable.
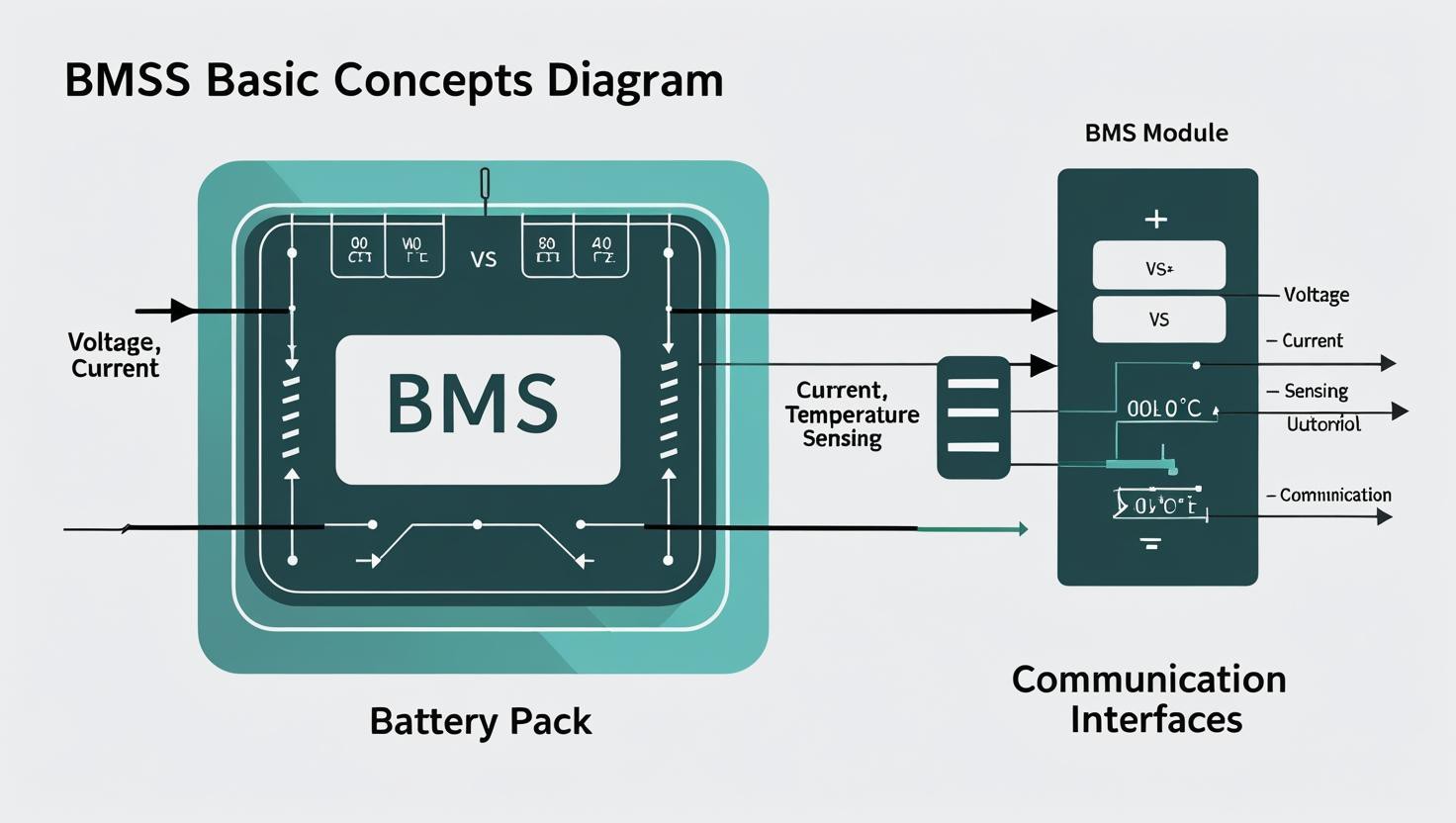
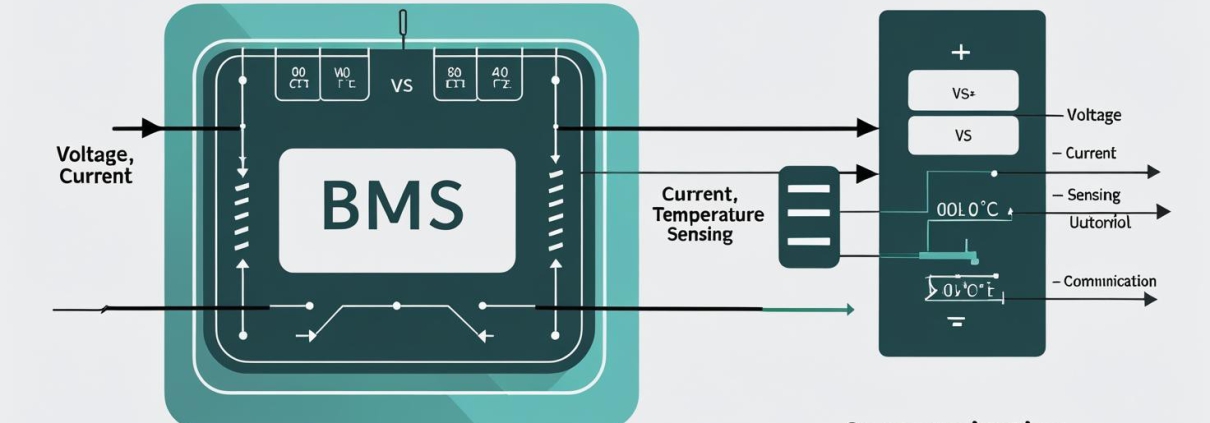
BMS Basic Concepts Diagram
- Core Functions of a Lithium Battery BMS
The lithium battery BMS is not just a simple safety switch. It’s a complex system with multiple roles:
2.1 Voltage Monitoring
Every cell in a lithium battery has a safe voltage range—typically 2.5–4.2 V for lithium-ion and 2.0–3.65 V for LiFePO₄. The BMS ensures no cell goes over or under these limits, preventing damage and safety hazards.
2.2 Current Control
Excessive charging or discharging current can cause overheating or internal damage. The BMS cuts off the circuit if current exceeds the safe limit.
2.3 Temperature Management
The BMS constantly reads temperature sensors embedded in the battery. If it detects overheating or freezing conditions, it pauses operation.
For more details on temperature effects and cooling/heating technologies, see:
Advanced Lithium Battery Thermal Management.
2.4 Cell Balancing
Over time, cells in a battery pack can drift apart in voltage. Balancing ensures each cell stays at similar charge levels, preventing capacity loss and extending battery life.
2.5 Communication and Data Logging
In smart systems, the BMS sends data to a display or app—showing state of charge (SOC), state of health (SOH), and error codes.
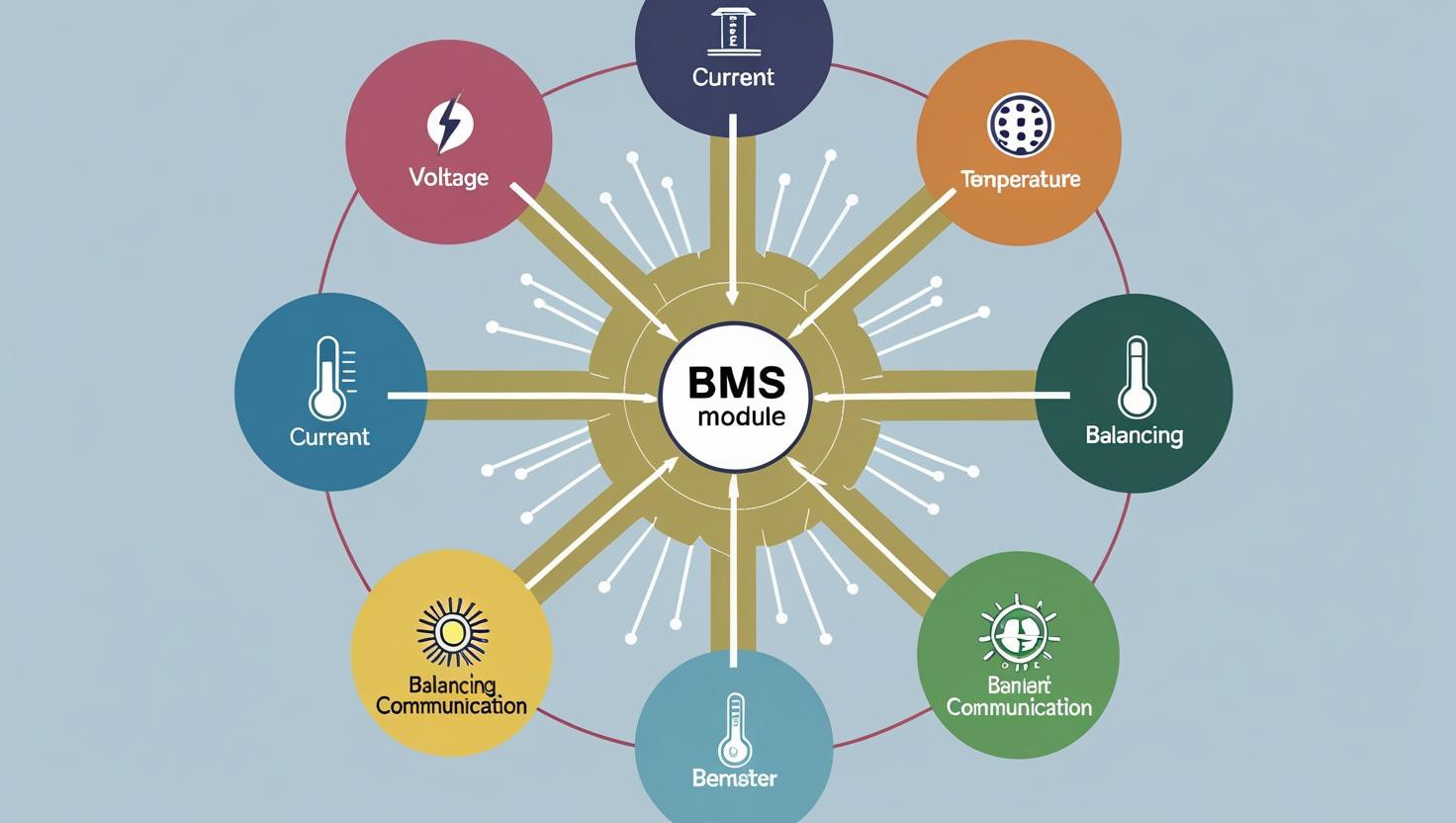
BMS functional decomposition
- Do All Lithium Batteries Have a BMS?
Do all lithium batteries have a BMS? Not necessarily.
| Battery Type | BMS Included? | Notes |
| EV battery packs (cars, buses, motorcycles) | Yes | Safety-critical. |
| Solar energy storage batteries | Yes | Large capacity, safety priority. |
| Small electronics (phones, laptops) | Yes (integrated) | Built into device circuits. |
| Individual lithium cells (e.g., 18650) | No | External BMS needed for packs. |
| Cheap generic battery packs | Sometimes missing | Risky without BMS. |
Operating lithium batteries without a BMS is risky because manual monitoring is impractical.
BMS Application
- Do You Need a BMS for Lithium Batteries?
Yes, in nearly all practical applications.
Reasons include:
- Safety – Prevents thermal runaway and electrical faults.
- Longevity – Protects against overcharge and deep discharge.
- Performance – Balances cells for consistent output.
For guidance on safe lithium battery storage, see:
How to Store Lithium Batteries Safely and Efficiently.
- How to Charge a Lithium Battery with BMS
Follow these steps:
- Use a charger matched to voltage and chemistry.
- Connect normally; BMS manages charging cutoff.
- Never bypass the BMS.
- Avoid extreme temperatures during charging.
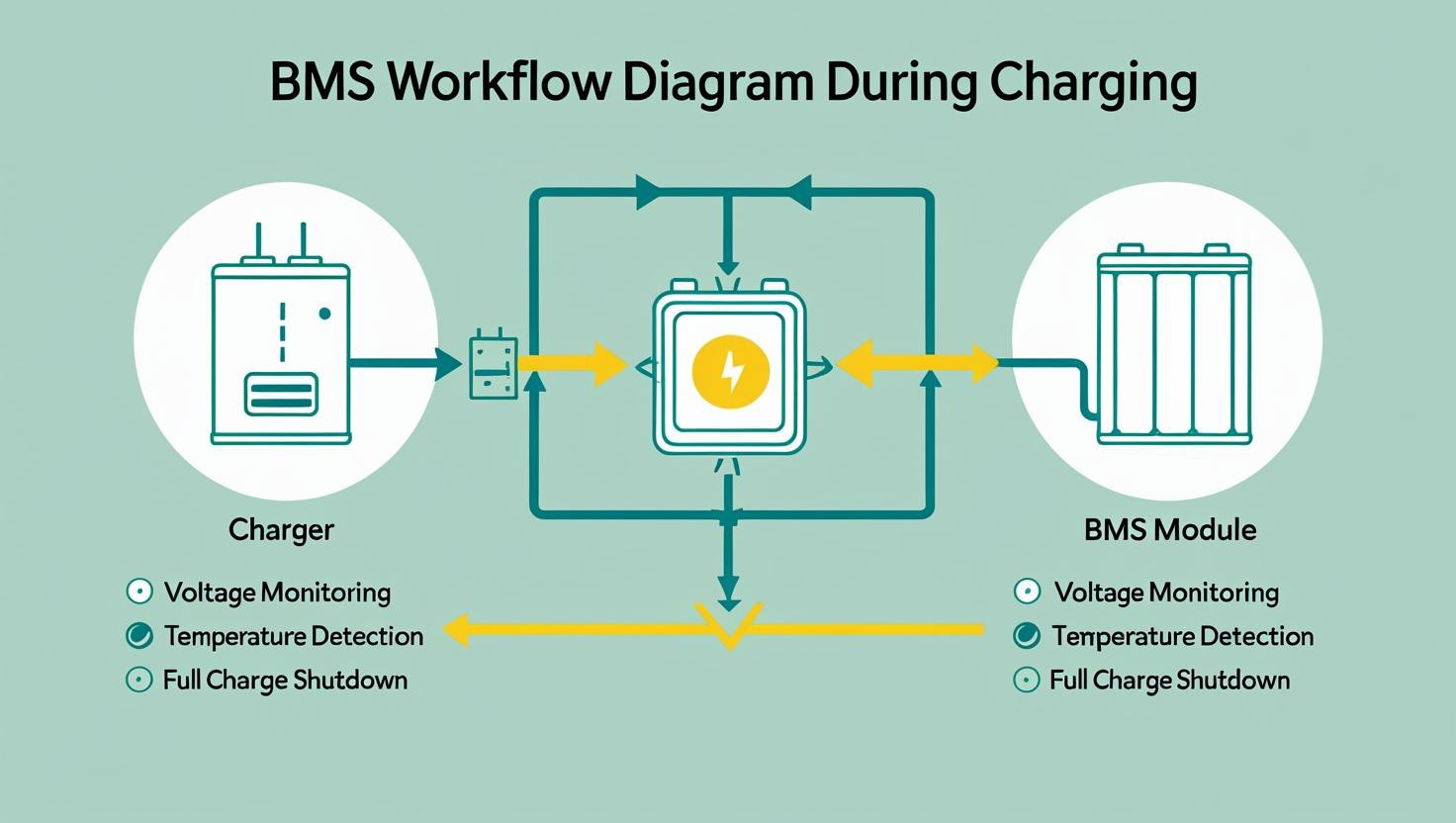
BMS Workflow Diagram During Charging-4
- Common Misconceptions About BMS
| Misconception | Truth |
| “If my charger is safe, I don’t need a BMS.” | False – BMS protects discharge and prevents faults. |
| “All BMS units are the same.” | No – They vary in features and capacity. |
| “BMS shortens battery life.” | Wrong – It extends battery life by protecting cells. |
- Choosing the Right BMS
Consider:
- Voltage rating matching battery pack
- Current rating fitting load requirements
- Balancing method: passive or active
- Extra features like Bluetooth or CAN bus monitoring
- Key Takeaways
- BMS is the “brain” managing battery safety and performance.
- Almost all lithium batteries need one.
- Proper charging with BMS ensures longevity and safety.
Schematic Diagram of The BMS’s Location In a Battery System